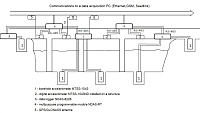
2025: 32-bit data logger for stationary observation posts
R-sensors presents a new seismic data logger that is NDAS-8436N.
This 32-bit data logger contains 6 high-resolution ADCs, a precision reference voltage source, a test signal generator, a GPS/GloNASS receiver, and a clock generator with frequency adjustment.
The control of the ADC chips, the acquisition and processing of signals are carried out through a single-board Beaglebone Green computer running the DEBIAN Linux operating system. The data logger is capable of operating with a wide input power range: from 7.5 to 60 V with an average power consumption of 1.5 to 3.0 W depending on the configuration.
In addition to the built-in filters of the microcircuit, the data logger software contains digital anti-aliasing filters with a decrease in the sampling rate by 2, 4 and 10 times. The combination of such filters provides sampling rates from 1 to 4000 sps.
The software allows performing offline registration (miniSeed, ASCII, binary) and streaming data (Seedlink) in real time.
Along with standard one-second packages, the data are transferred in reduced packages with a duration of 0.1 seconds. When using filters with a minimum phase response, this reduces the delay time and makes the use of this data logger especially effective for monitoring and early warning systems.
Seismic data are stored in a modern miniSEED v3 format on an external USB drive and SD-card for reliable and convenient storage.
Using SeedLink v4 with a package size of 100 ms allows quickly and reliably transferring data over Ethernet in real time.
It is possible to connect analog instruments by R-sensors and analog instruments by various manufacturers.